

This can be quicker and much less taxing on resources than a full rendering of the company's accounts, ultimately saving the company extra costs when employing financial advisors or accountants. When tracking just the initial cost of an asset, an accountant may only need to verify the initial cost value of the company's assets. The longer an accountant works to verify and finalize a company's financial reports, the more it can cost the company. When a business employs a financial advisor or accountant, it might undergo additional expenses for these services. The historical cost principle refers to recorded values that are objective and verifiable as sales receipts, bank transactions or invoices, which are used to easily confirm the original value of an asset at purchase.
#ACCOUNTING PRINCIPLES DEFINITION UPDATE#
This is because the historical cost principle only requires the initial cost of an asset, and a business may not need to continuously update its financial records to show current market values. Ease of financial record-keepingīecause the cost principle is merely the initial cost of an asset, it can be much easier to keep a record of this initial value. Some of these advantages include the ease of tracking, the objectivity of the cost principle and the actual cost of utilizing financial services to calculate historical cost principles of a company's assets. The simplistic nature of recording the cost principle means that there are a few key advantages to keeping financial records of the initial costs of assets. Read more: Q&A: What Does "Fiscal Year" Mean? Advantages of the cost principle Additionally, the cost principle is also referred to as the historical cost principle, meaning that no matter the appreciation or depreciation an asset goes through over time, the original cost of the asset at the time of acquiring is the value that is kept as the cost principle. Oftentimes, the financial records may track the depreciation or growing value of acquired assets, however, the cost principle will remain the same. Assets that are recorded can include short-term and long-term assets, liabilities and any equity, and these assets are always recorded at their original cost. The amount of the asset that is recorded may not be increased for improvements in market value or inflation, nor can it be updated to reflect any depreciation. The cost principle is an accounting principle that records assets at their respective cash amounts at the time the asset was purchased or acquired.

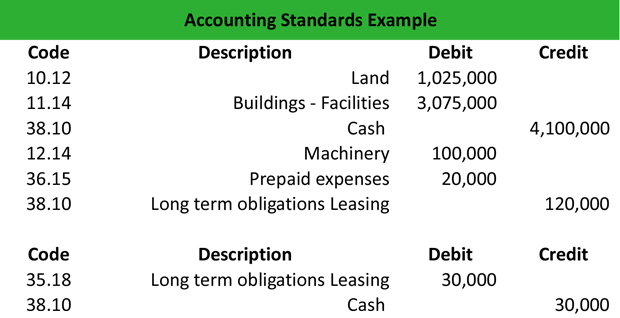
In this article, you will learn what the cost principle is, the advantages and disadvantages of the cost principle and how it can be applied to a business through the use of relevant examples. Often, the cost principle is used to keep a record of a company's tangible assets, without reflecting the market value. This initial value is called the cost principle, and it is an important aspect of financial reporting for many companies. When a business acquires an asset, the value of that asset is recorded in the business's financial reports.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
